深入探究一下Kubernetes Operator Pattern,为CustomResourceDefinition使用贡献有效经验
Kubernetes让部署和无感知扩容变的异常简单。如果实操,基本上只需要在YAML文件中把相关联的应用的参数做下指定即可,然后提交给Kubernetes系统识别你的声明式指令,Kubernetes内建的状态循环机制就会自动的创建或者销毁相应资源,来把集群调整到我预设的状态上来,一切都如此轻松!
然而,你可能也听说过,Kubernetes最强大的地方在于它的可扩展性。这篇文章目的就是带大家了解一下Kubernetes的Operators pattern,看看Kubernetes的哪些部分参与了Operators实现,是什么让Operator与Kubernetes如此完美的融合,仿佛就像Kubernetes的内建系统一样丝滑。
kubernetes的objects和controller">Kubernetes的Objects和Controller
Kubernetes中的一切似乎都围绕着objects和controller。
Kubernetes中的对象,比如说Pod,Namespace,ConfigMap或者Event,它们在Kubernetes系统上都是持久化的entity。Objects常被作为某种“意图的记录”,通过创建或者消除对象,我们可以把Kubernetes调整到我们预计的状态。
Objects有点类似于数据结构。
另一方面,controllers无休止的循环,监控着集群实际和预期的状态,当两者不一致时,controller就开始做调整,把集群调整到预设状态。
Controllers这里就有点像算法。
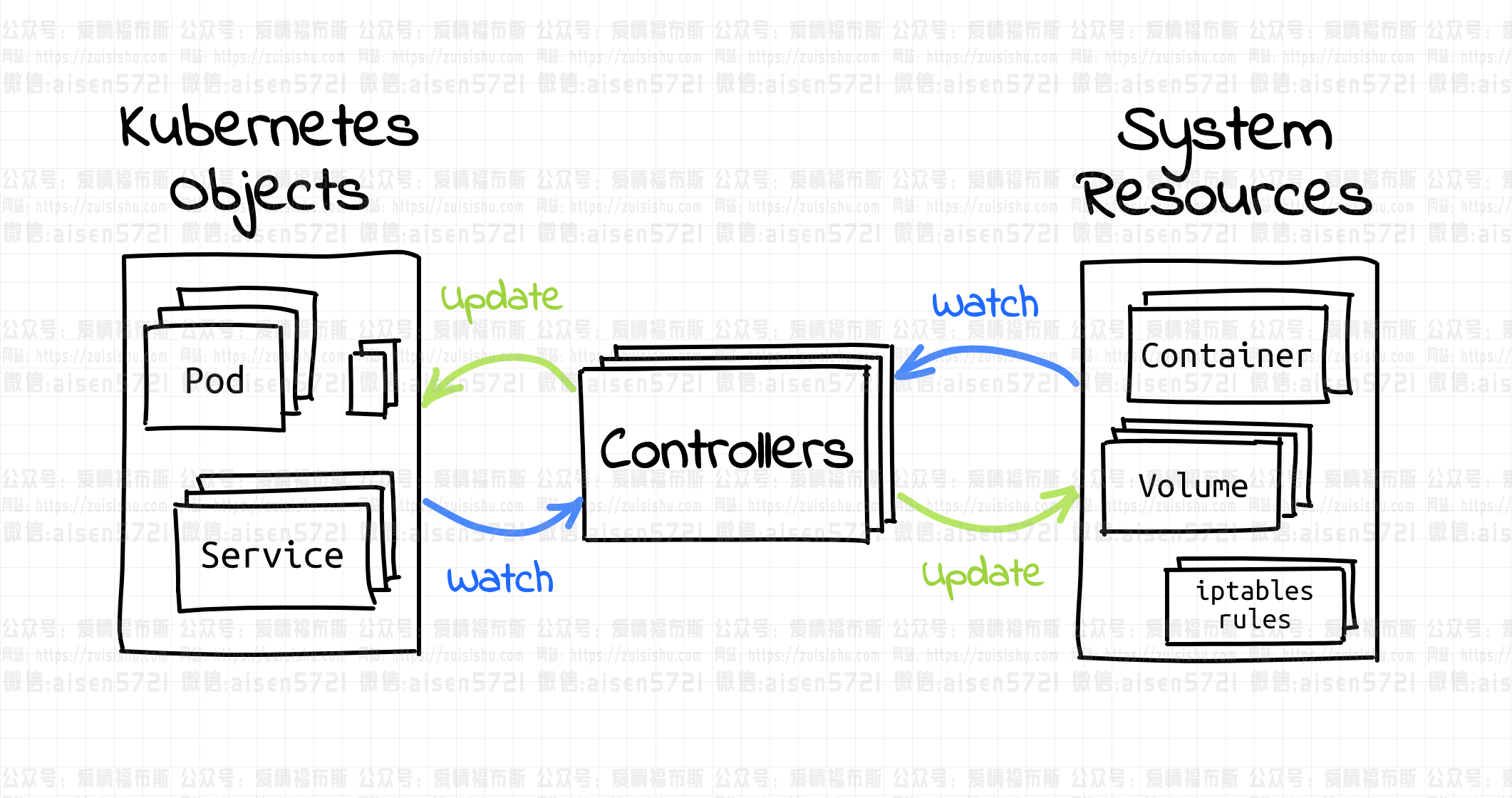
后面的部分我们会深入探究Controller,目前我们把重点放在Object上。
kubernetes的api结构">Kubernetes的Api结构
所有与Kubernetes Object直接或间接的交互,都是通过Kubernetes API,可以认为Kubernetes API是软件设计里一件高度结构化的杰作!
有数以亿计的文档都在写Kubernetes API及其相关主题,为了讲的更清楚,我花费了大量时间来设计我这篇文章的讲解条理。因为我们即将谈到的Kubernetes Operator pattern,它是重度依附于Kubernetes API才具备的能力,因此搞清楚Kubernetes的设计很重要。这里我从Kubernetes API文档中摘下来的简介:
Kubernetes offers a RESTful declarative HTTP API. Still remember those Kubernetes objects? A collection of objects of a certain kind form an API resource:
A resource is an endpoint in the Kubernetes API that stores a collection of API objects of a certain kind; for example, the built-in pods resource contains a collection of Pod objects.
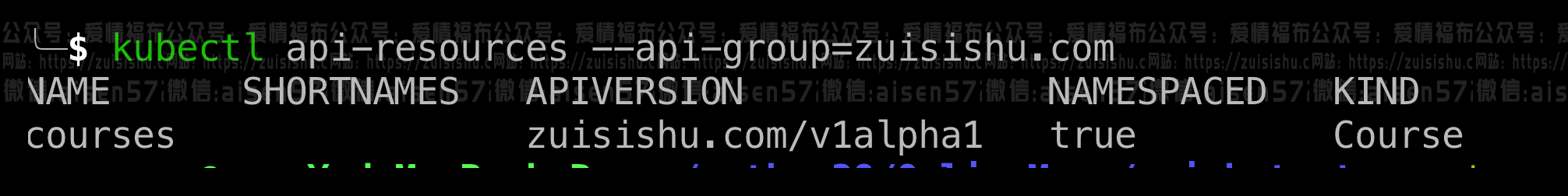
你可以用命令:kubectl api-resources来获取可用的资源列表:
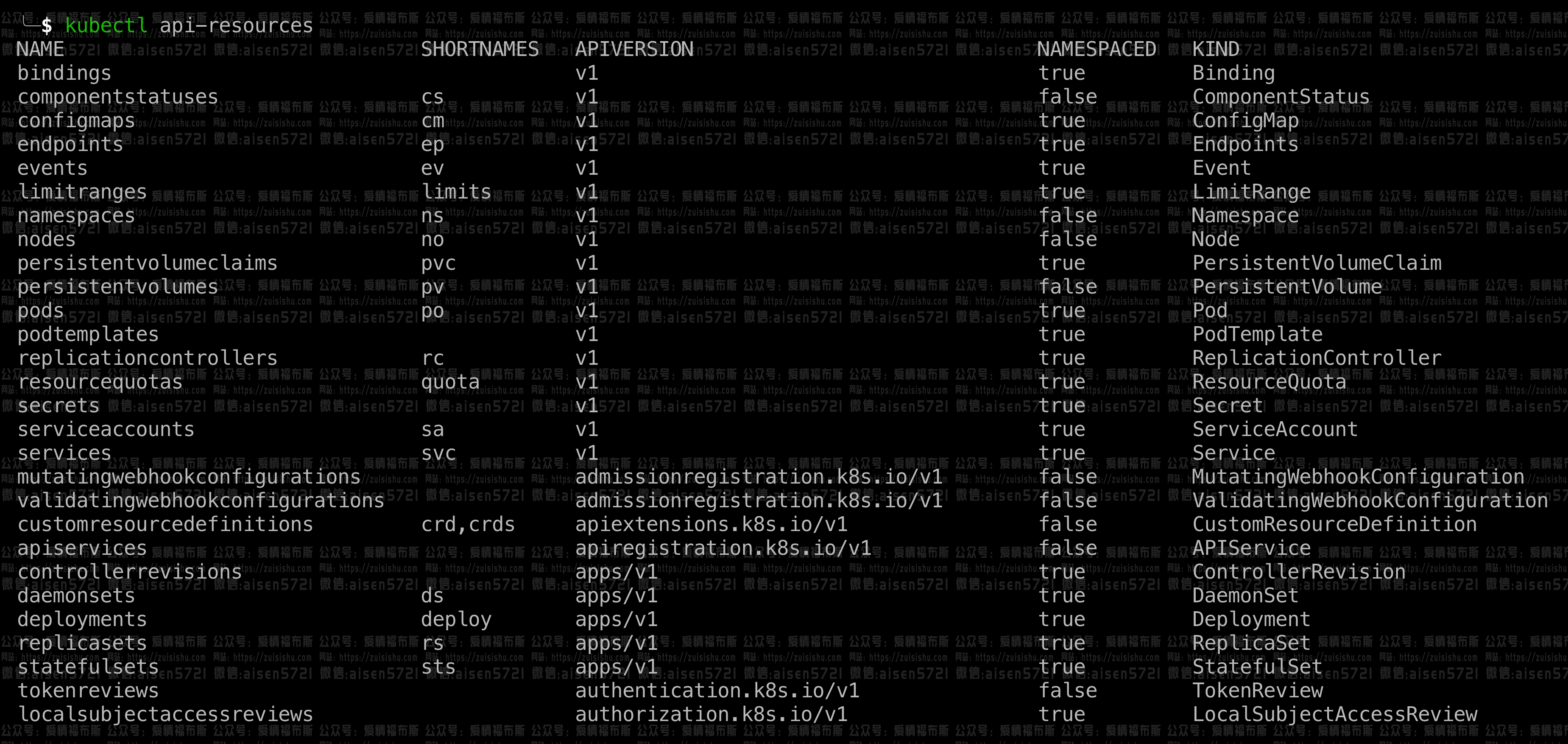
给我们响应也资源列表,但随之,问题也出现了,Kubernetes如何迅速的迭代,如果一个新的attribute需要添加进现有的resource definition中该怎么办?毕竟API versioning一直都是出雷重灾区!
显而易见, Kubernetes API中,以/api/<version>/<resource>为前缀的结构是所有API resources都一致的。因此针对于某个resource的修改会导致整个API资源的版本冲突。你想高度定制的resources越多,这种矛盾越突出!
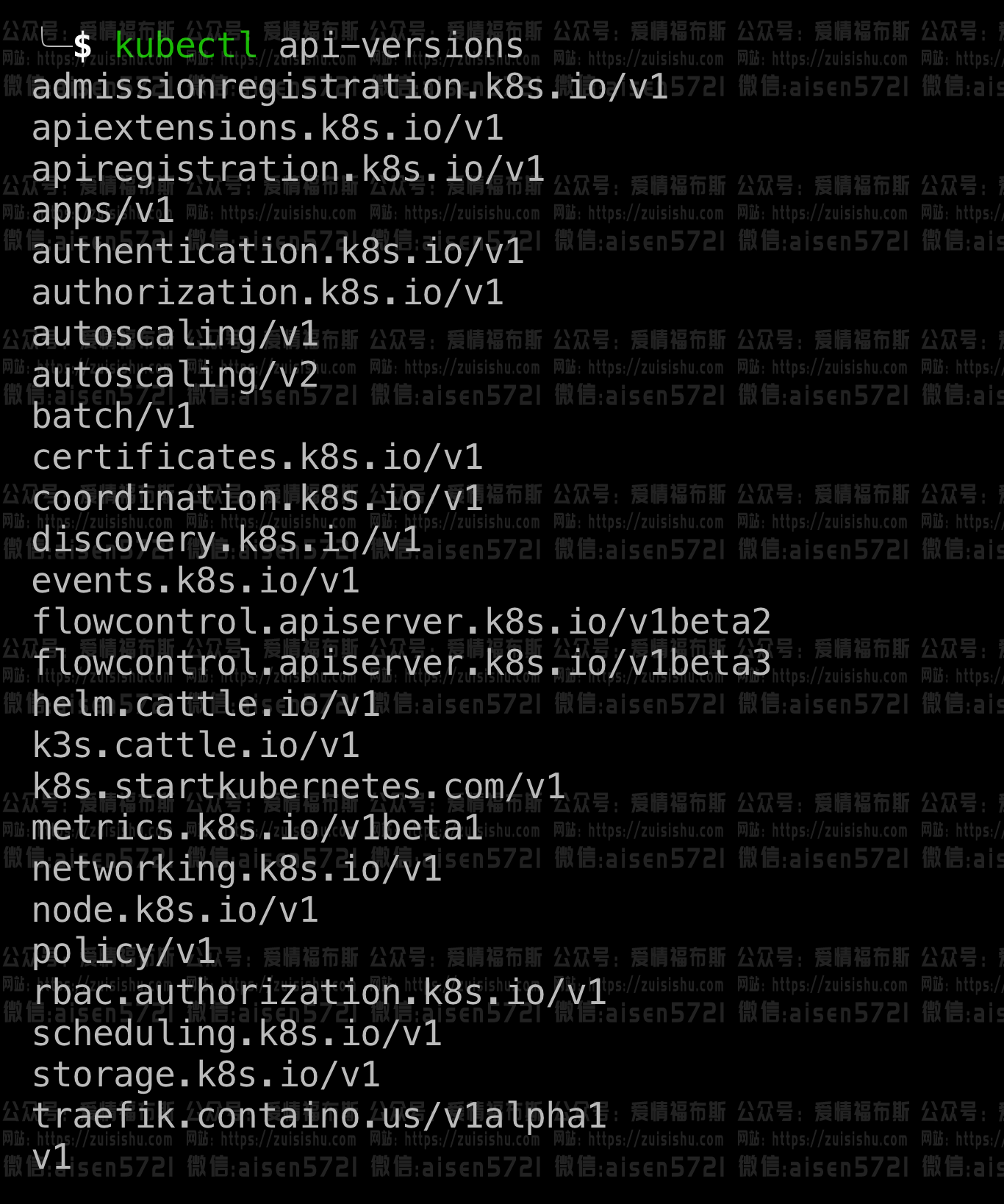
API组横空出世!A bunch of related resources forms an API group:
To make it easier to evolve and to extend its API, Kubernetes implements API groups that can be enabled or disabled.
你也可以通过命令:kubectl api-versions获取所有可用的API groups及其版本:
Kubernetes中,objects类似,也是基于名称被调度的。所以,如果你起了两个Pod,它们名字都是唯一的。但因为集群可能特别庞大,又要保证在集群之内名字唯一,需要一种机制来避免冲突。像一个物理集群上有大量的逻辑集群,namespace就出现了。
ubernetes supports multiple virtual clusters backed by the same physical cluster. These virtual clusters are called namespaces. … Namespaces provide a scope for names. Names of resources need to be unique within a namespace, but not across namespaces. Namespaces cannot be nested inside one another and each Kubernetes resource can only be in one namespace.
因此,API group、resource type、namespace、name整体组合就用来鉴权API objects。
是不是开始糊涂了,不要急,下面这张图表给你🙈。

此处先来个简短的总结,我们大概谈了一下objects,groups,namespace,说好的按自定义思路做扩展哪去啦?
💡要注意,resource偶尔也会有object或者API endpoint的含义(反之则不然),它是context敏感的!
kubernetes-custom-resources">Kubernetes Custom Resources
似乎要保持Kubernetes API有条理但又具备灵活的扩展性需要大量的精力投入。
我这里用到的条理一词,你知道意味着什么吗?Kubernetes API包含着很多endpoints叫做resources。这些API resources着一系列共同的要求,描述上面具有专有性和可操作性,也即大家所熟知的RESTful CRUD,具有相对不频繁更新、适度的数据量、名称具有valid DNS subdomains等特点。
这些限制让这些resource workflows特征统一。举例,你在处理一系列的Pods时,及在处理Services,Nodes,或者RBAC roles时,用的都是get,describe或者update这同一种行为。
$ kubectl get pods
$ kubectl get services
$ kubectl get roles
$ kubectl describe pods # or services, or roles
$ kubectl edit pods # or services, or roles
不只kubectl受益于这种统一,如下的完整列表都具有这种统一的命令特征:
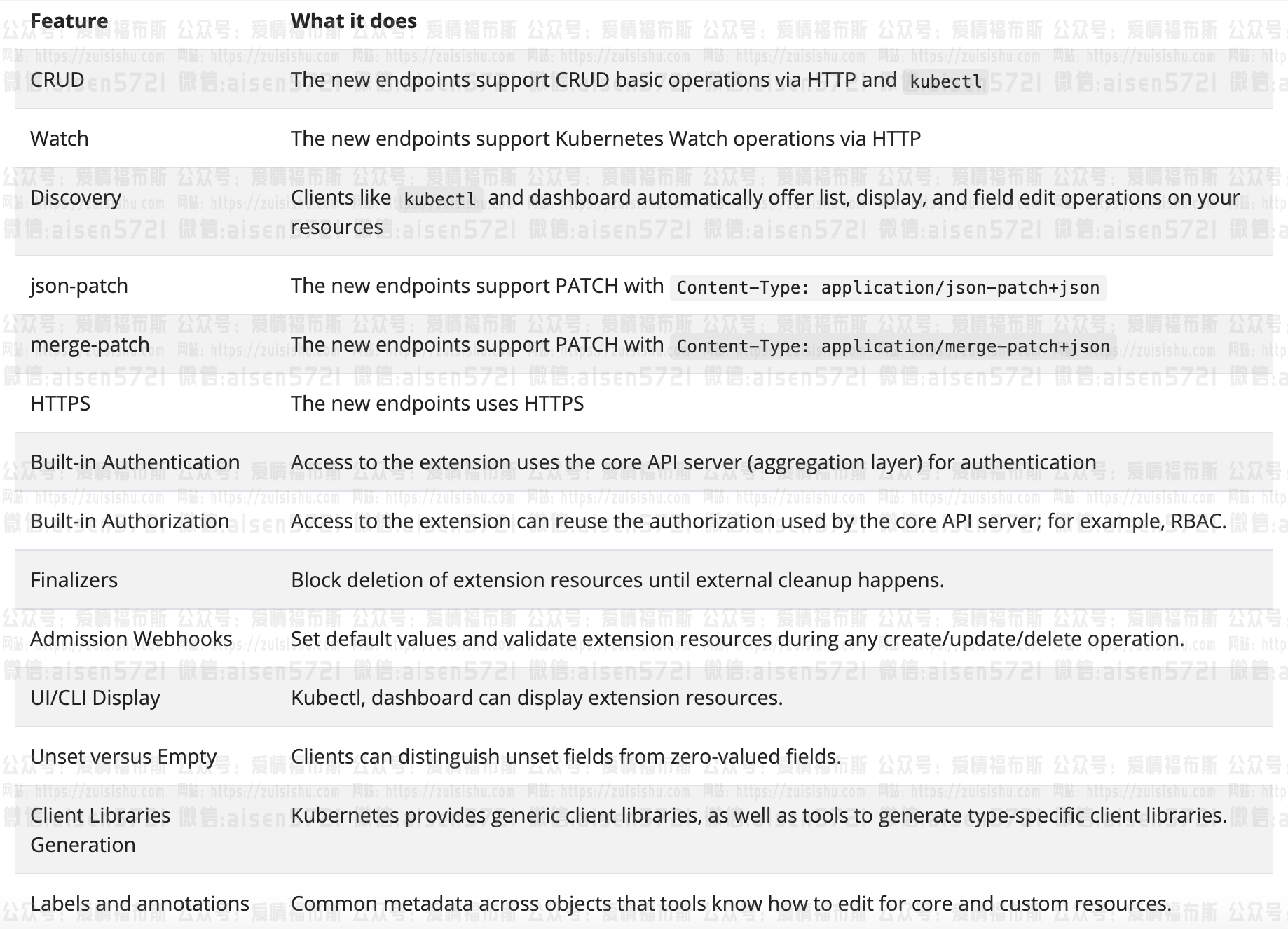
非常统一,极具智慧,不是吗?
如果依照我过去的思路,要扩展API,对我来说,有相当广泛的理由,希望我扩展应用的endpoints可以从这种通用的功能定义中获益,但是那样做意味着要达到这种API的扩展效果需要添加更多的resources!
而实际上,Kubernetes中,我们可以轻轻松松来注册custom resources。这个过程是实时响应且不需要重启和更新API server的。
这种custom resources怎么添加?Kubernetes早就未雨绸缪了,通过与已存在的resources间来交互,让向kubernetes系统中添加custom resource如此丝滑!而这个特定的API resource叫做CustomResourceDefinition(CRD):
The CustomResourceDefinition API resource allows you to define custom resources. Defining a CRD object creates a new custom resource with a name and schema that you specify.
还可以参考这篇:
When you create a new CustomResourceDefinition (CRD), the Kubernetes API Server creates a new RESTful resource path for each version you specify.
如何创建Custom Resource
记住,resource就是特定类型的kubernetes object。从规范上来说,objects就具有相应的属性。所以,我们的CustomResourceDefinition应该更多关注于我们特定resource的属性描述上面。另外,要了解到,custom resources是具有namespace和cluster隶属约束的。CRD的scope字段就是这种特征的体现。
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: course.zuisishu.com
spec:
group: zuisishu.com
names:
kind: Course
listKind: CourseList
plural: courses
singular: course
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
schema: ...
...
完整版本,且可执行:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: courses.zuisishu.com
spec:
group: zuisishu.com
names:
kind: Course
listKind: CourseList
plural: courses
singular: course
scope: Namespaced
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
schema:
openAPIV3Schema:
description: Course is a custom resource exemplar
type: object
properties:
apiVersion:
description: 'APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation
of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest
internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources'
type: string
kind:
description: 'Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this
object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client
submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In PascalCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds'
type: string
metadata:
type: object
spec:
description: CourseSpec is the spec for a Course resource
type: object
properties:
title:
type: string
author:
type: string
status:
description: CourseStatus is the status for a Course resource
type: object
properties:
publishedAt:
type: string
served: true
storage: true
subresources:
status: {}
status:
acceptedNames:
kind: ""
plural: ""
conditions: []
storedVersions: []
EOF
相信如果你经常玩k8s的话,那么执行命令kubectl apply等应该不陌生。
也可以简单对于刚生成的resource做下检验:
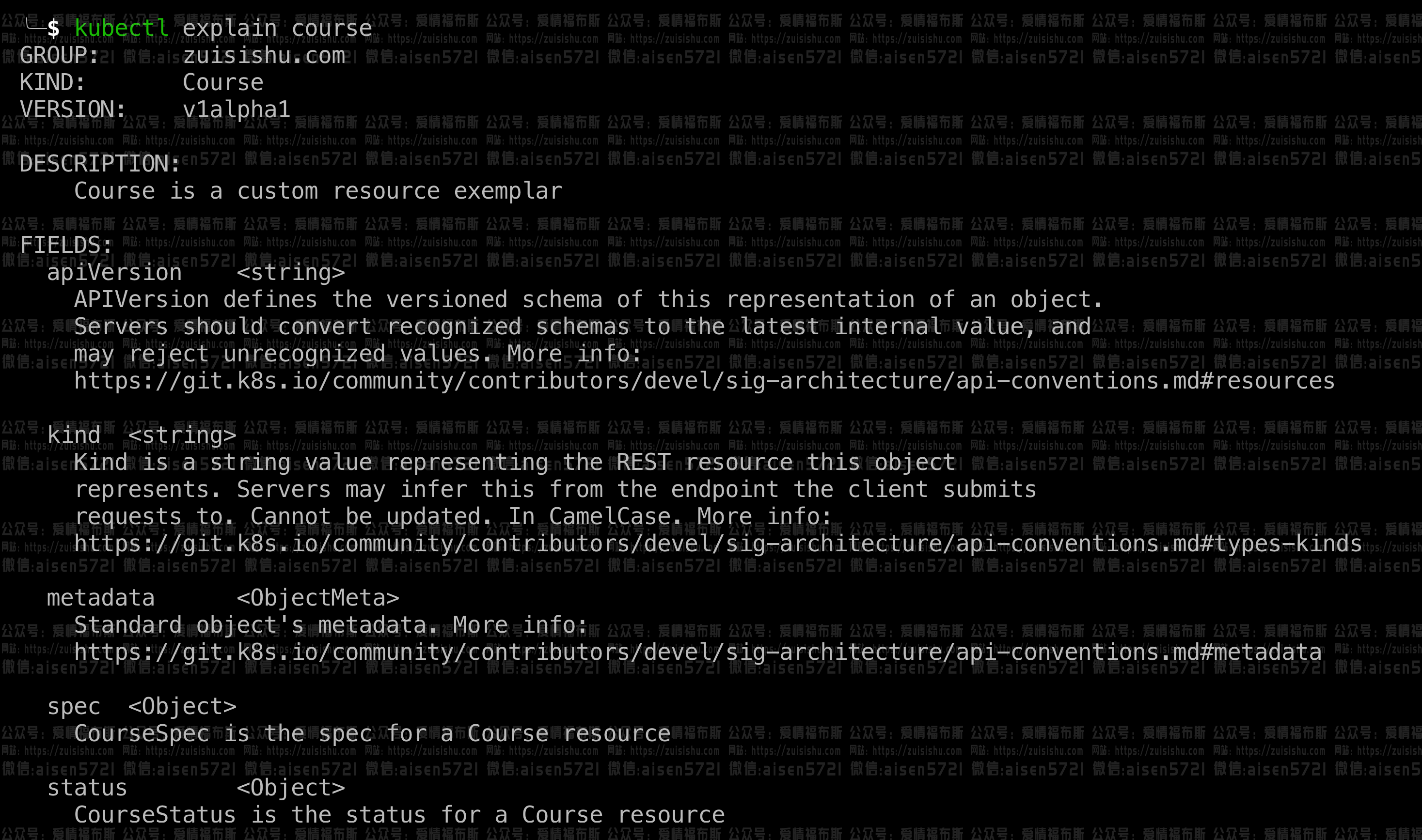
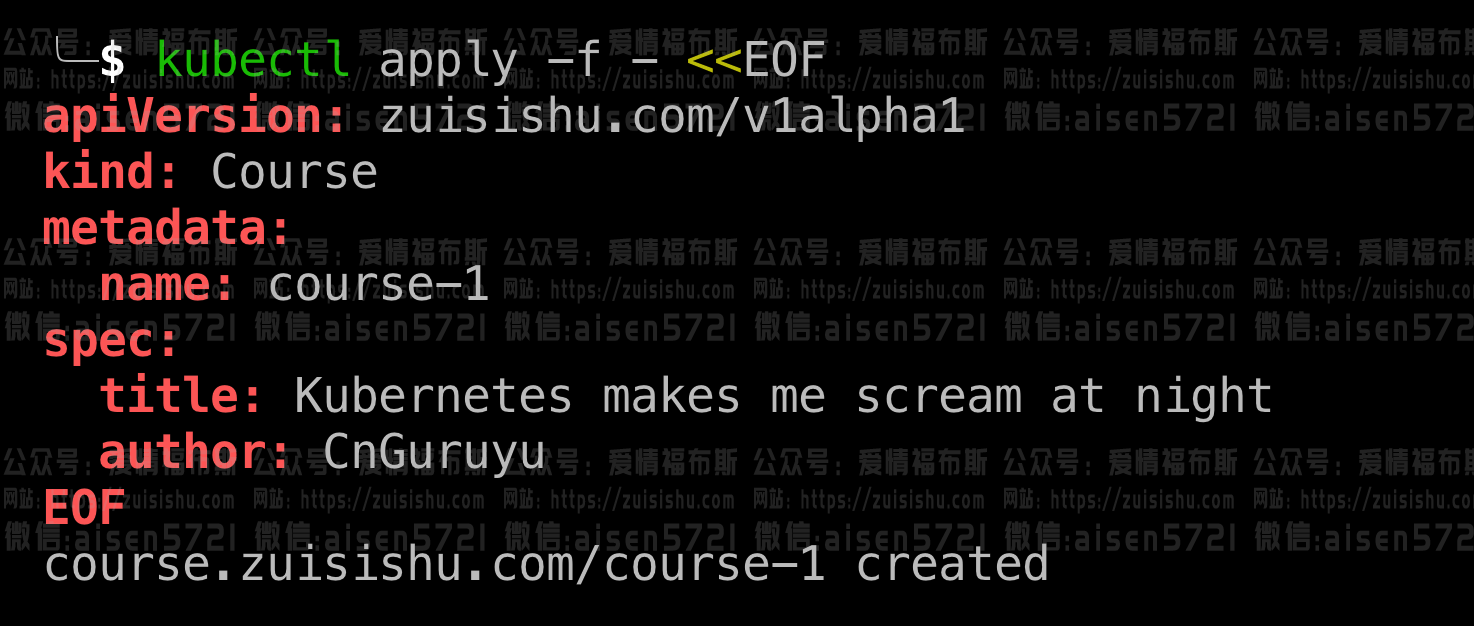
做完上一步,我们已经可以创建Course类型的object了:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: zuisishu.com/v1alpha1
kind: Course
metadata:
name: course-1
spec:
title: Kubernetes makes me scream at night
author: CnGuruyu
EOF
操作下已创建出的对象:
 当然啦,能建就能删:
当然啦,能建就能删:

所以我们可以通过动态注册Custom Resource的方式扩展Kubernetes API,并让这个Custom Resource就像内置的resources一样,有没有感觉我前面的举例还挺恰当的,Kubernetes all kinds of Ojbects就像数据结构,而这种扩展能力就像你掌握了某种算法,让你更好利用数据结构来提升执行效率!
kubernetes-crds对比custom-api-server">Kubernetes CRDs对比Custom API Server
显而易见,CRD并非扩展Kubernetes API的唯一途径。它也可以用aggregation layer的方式,结果也得到一系列的custom resources。然而,关于aggregation layer,我发现没有一个这项技术的实战应用,也没有任何鲜活的教程。这里留个坑,以后再埋。
kubernetes-operators">Kubernetes Operators
Custom Resources非常简洁易懂,但是单纯定义它没有任何意义,你需要自定义代码逻辑,来与其交互。
On their own, custom resources simply let you store and retrieve structured data. When you combine a custom resource with a custom controller, custom resources provide a true declarative API.
你可能记得,Kubernetes中的逻辑是以控制器形式组织的。有着巨大的内建controller实时监控着内建resources,以及对cluster apply相应变更操作。但我们怎么获取custom controller呢?
很明显,启用一个Pod,接着需要做的就是挑一门你擅长喜欢的编程语言,编写一个controll loop,接着把代码打包进Docker镜像,再部署到cluster中即可。
所以,到底什么是Kubernetes Operator?再次引用下官方文档:
an operator is a client of the Kubernetes API that acts as a controller for a Custom Resource.
简洁明了。当然你也可以通过添加多个Custom Resources来偏离这个定义,但是写Operator的最佳实践就是每种资源一个Controller,让resources的受控关系明确清晰。
什么样的逻辑写在Operator中更适合呢?构通常怎么理解Pattern?通过操作应用来做一些有特定规律的事,举例:
- deploying, backuping, restoring, or upgrading应用
- 把 Kubernetes service暴露给non-Kubernetes应用
- 工程学
- 分布式应用自动选主
但怎么可能就有这么点用处,所以以上只做举例!毕竟想象无限,机会无限!
kubernetes-operator举例">Kubernetes Operator举例
拿我比较喜欢的operators来举例, inlets-operator。这个operator是个很好的跳出常规思维的例子。这个operator会用分配public IPs的方式把你集群内的deployment向公网暴露。之所以可行,是能积极监测集群中为LoadBalancer类型的Kubernetes Service。每个该类型的service,它就使用inletsctl工具,在你云厂商的主机上提供一个VM。VM就绪以后,operator就使用Inlets Tunnel将它与辅助部署连接起来。这实际就让本地部署具备了类似于云端部署LoadBalancer这样的特性。

更详细的分析,后面再补文章。
总结
谈到operators,绝大多数时候,是运行在custom controller上一个或几个pod,或者更多与它交互的custom resoureses。
本文,我们主要讲了对于Kubernetes扩展性起到核心支持作用的Kubernetes API。你可以把任意的逻辑放到你自定义的operator里,这样就可以像与Kubernetes内建resoures交互的方式来与operator交互。因此,内置命令行工具kubectl的存在,由于开箱即用,如果以此思路来开发相应扩展工具,也更符合kubernetes用户的使用经验。甚至应该也可以在现有的operator之上构建operator,或者重用完全相同的custom API resources 机制,使不同的operators相互交互。



